Personalized medicine is at the forefront of a healthcare revolution, shifting the paradigm from a “one-size-fits-all” approach to tailored treatments that consider an individual’s unique genetic makeup. This innovative approach not only enhances the effectiveness of medical interventions but also minimizes adverse effects, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
What is Personalized Medicine?
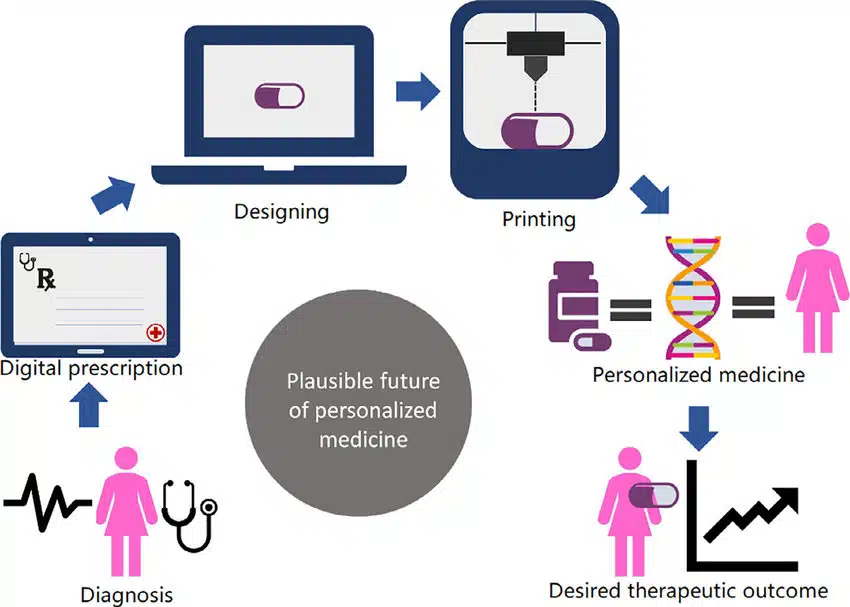
Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, is an emerging field that utilizes a patient’s genetic profile, lifestyle, and environmental factors to guide healthcare decisions. By understanding the specific characteristics that make each patient unique, healthcare providers can tailor prevention strategies, diagnoses, and treatments to meet individual needs. This approach is made possible through advancements in genomics and biotechnology, which allow for more accurate predictions about how patients will respond to various treatments.
Key Components of Personalized Medicine
- Genetic Profiling: Analyzing a patient’s DNA helps identify genetic predispositions to certain diseases, enabling proactive management and tailored treatment plans.
- Targeted Therapies: Treatments are designed to target specific genetic mutations or pathways involved in disease progression. For example, certain cancer therapies are effective only for patients with specific tumor markers.
- Preventive Strategies: Personalized medicine emphasizes prevention by identifying risk factors early and implementing lifestyle changes or interventions that can mitigate these risks.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Advances in technology allow for continuous monitoring of patients’ health data, enabling timely adjustments to treatment plans based on real-world effectiveness.
Benefits of Personalized Medicine
1. Improved Treatment Efficacy
By tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles, personalized medicine increases the likelihood of successful outcomes. For instance, cancer treatments that target specific genetic mutations have shown significantly higher success rates compared to traditional therapies.
2. Reduced Side Effects
Personalized approaches can minimize adverse reactions by ensuring that patients receive medications that are more compatible with their genetic makeup. This reduces the trial-and-error process often associated with standard treatments.
3. Enhanced Preventive Care
With insights gained from genetic testing, healthcare providers can offer preventive measures tailored to an individual’s risk factors, potentially preventing diseases before they manifest.
4. Cost Efficiency
By improving treatment success rates and reducing hospitalizations due to adverse drug reactions or ineffective therapies, personalized medicine can ultimately lower healthcare costs for both patients and providers.
5. Empowerment Through Knowledge
Patients who engage in personalized medicine often feel more empowered regarding their health decisions. Understanding their genetic risks allows them to take proactive steps in their health management.
Also Read : What Are The Latest Advances In Medical Technology?
Conclusion
Personalized medicine represents a significant advancement in healthcare, moving away from generalized treatment protocols towards individualized care that considers each patient’s unique characteristics. As research continues to evolve and technology advances, the potential for personalized medicine to transform patient outcomes is immense. By focusing on prevention, targeted therapies, and patient empowerment, personalized medicine is set to revolutionize how we approach health and wellness.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between personalized medicine and traditional medicine?
Traditional medicine often uses a one-size-fits-all approach based on population averages, while personalized medicine tailors treatments based on individual genetic profiles and other personal factors.
Q: How does genetic testing work in personalized medicine?
Genetic testing involves analyzing a sample of blood or saliva to identify specific genes or mutations that may influence disease risk or treatment response.
Q: Is personalized medicine only applicable to cancer treatment?
No, while it has made significant strides in oncology, personalized medicine applies to various fields including cardiology, psychiatry, and rare genetic disorders.
Q: What role does technology play in personalized medicine?
Technology facilitates the collection and analysis of vast amounts of health data, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on real-time patient information.
Q: Are there any risks associated with personalized medicine?
Potential risks include privacy concerns regarding genetic data and the possibility of misinterpretation of test results. It’s essential for patients to discuss these aspects with their healthcare providers.
Q: How can I access personalized medicine services?
Many healthcare institutions now offer personalized medicine services; you can inquire with your primary care physician or seek out specialized clinics focused on this approach.
Q: Is personalized medicine covered by insurance?
Coverage varies by insurance provider and plan; it’s advisable to check with your insurer regarding coverage for genetic testing and related services.
Q: What are biomarkers in the context of personalized medicine?
Biomarkers are biological indicators (such as proteins or genes) used to assess health conditions or predict responses to treatments in personalized medicine.