In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, health literacy has taken on new dimensions, particularly with the rise of digital technologies. The ability to access, understand, and utilize health information from electronic sources is crucial for making informed health decisions. This article explores the challenges and opportunities presented by health literacy in the digital age, emphasizing the importance of digital health literacy in promoting better health outcomes.
Understanding Health Literacy in the Digital Age
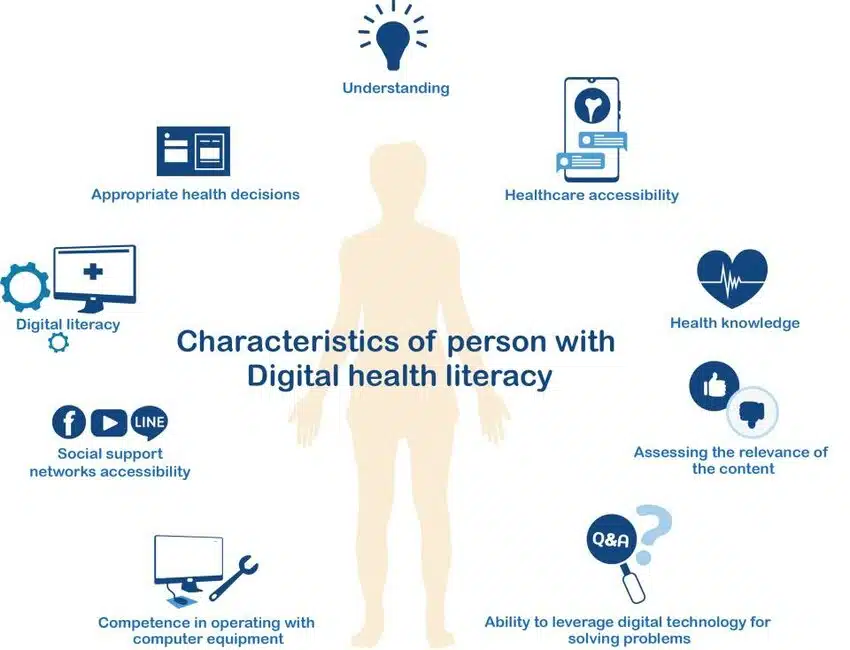
Health literacy traditionally refers to the capacity of individuals to obtain, process, and understand basic health information needed to make informed decisions about their health. In the digital age, this concept has expanded to include digital health literacy (DHL), which encompasses the skills required to navigate digital platforms effectively. DHL involves not only traditional literacy but also information literacy, media literacy, and computer literacy.
Key Components of Digital Health Literacy
- Traditional Literacy: The foundational ability to read and comprehend text.
- Information Literacy: Understanding how to locate and evaluate health information.
- Scientific Literacy: The capability to contextualize health-related findings within a broader scientific framework.
- Media Literacy: The skill to critically assess information presented through various media channels.
- Computer Literacy: Proficiency in using digital tools and technologies to access health information.
- Health Literacy: The ability to apply health information effectively to promote personal and community health.
Challenges of Health Literacy in the Digital Age

Despite the potential benefits of digital health resources, several challenges hinder effective health literacy:
1. The Digital Divide
Access to technology is not uniform across populations. Many individuals, particularly those in rural or low-income areas, lack reliable internet access or the devices necessary to engage with digital health platforms. This disparity creates a significant gap in health information access and utilization.
2. Misinformation and Complexity
The internet is rife with misinformation regarding health topics. Individuals with low digital health literacy may struggle to discern credible sources from unreliable ones, leading to confusion and potentially harmful decisions regarding their health.
3. Complex Navigation
Many digital health tools and applications are not designed with user-friendliness in mind. Complex interfaces and medical jargon can overwhelm users, particularly those who are less tech-savvy or have lower levels of traditional health literacy.
4. Privacy Concerns
As more personal health information is shared online, concerns about data privacy and security have become paramount. Patients may hesitate to use digital resources due to fears of their sensitive information being compromised.
Opportunities for Enhancing Health Literacy
While challenges exist, there are numerous opportunities to improve health literacy in the digital age:
1. Telemedicine and Remote Care
The rise of telemedicine has made healthcare more accessible than ever before. Patients can consult healthcare providers remotely, reducing barriers related to transportation and time constraints.
2. Health Apps and Wearables
Digital tools such as mobile health apps and wearable devices empower individuals to monitor their health actively. These technologies can provide personalized insights that encourage proactive management of one’s health.
3. Educational Initiatives
Health organizations can develop targeted educational programs aimed at improving digital health literacy among diverse populations. Offering training on how to navigate digital resources can enhance users’ confidence and competence.
4. User-Centered Design
Creating user-friendly applications that prioritize clear language and intuitive navigation can significantly improve engagement with digital health tools. Incorporating feedback from users during the design process ensures that these tools meet their needs effectively.
5. Community Engagement
Collaborative efforts involving community organizations can help bridge gaps in digital access and literacy by providing resources and support tailored to specific populations.
Also Read : How Teleradiology Is Revolutionizing Global Healthcare Access?
Conclusion
Health literacy in the digital age presents both challenges and opportunities that must be addressed to promote better health outcomes for all individuals. By enhancing digital health literacy through education, user-friendly technology design, and community engagement, we can empower individuals to navigate the complex landscape of healthcare more effectively. As we continue to integrate technology into healthcare delivery, prioritizing health literacy will be essential for fostering an informed population capable of making sound health decisions.
FAQs
1. What is digital health literacy?
Digital health literacy refers to the ability to find, understand, evaluate, and use health information from electronic sources effectively.
2. Why is digital health literacy important?
It enables individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare by accessing reliable information online, using telehealth services, and managing their own health through technology.
3. What challenges do people face regarding digital health literacy?
Challenges include limited access to technology (the digital divide), misinformation online, complex navigation of digital tools, and privacy concerns regarding personal data.
4. How can I improve my digital health literacy?
You can improve your skills by taking advantage of educational resources offered by healthcare organizations, practicing using various digital tools, and seeking assistance when needed.
5. What role do telemedicine services play in enhancing health literacy?
Telemedicine provides accessible healthcare options that allow patients to engage with providers remotely, helping them understand their conditions better without geographical barriers.
6. How does misinformation affect public health?
Misinformation can lead individuals to make poor healthcare decisions based on incorrect or misleading information found online.
7. Are there specific groups more affected by low digital health literacy?
Yes, older adults, low-income populations, rural residents, and those with lower educational attainment often face greater challenges in accessing and utilizing digital health resources.
8. What strategies can organizations implement to enhance digital health literacy?
Organizations can provide training programs on navigating digital platforms, create user-friendly applications with clear instructions, and engage communities through outreach initiatives.





