Financial accounting is a key part of accounting. It records and reports a company’s transactions over time. It prepares important financial statements like the balance sheet and income statement.
These statements show a company’s financial health and cash flow. They help investors, creditors, and others make informed decisions.
Financial accounting follows certain rules and standards. In the U.S., public companies use the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Internationally, many follow the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
These rules help keep financial reports consistent and clear. They make it easier for everyone to understand a company’s financial situation.
Key Takeaways
- Financial accounting is a crucial discipline that records, summarizes, and reports a company’s financial transactions and performance.
- Financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health and operations.
- Financial accounting is guided by established principles and standards, such as GAAP in the U.S. and IFRS internationally, ensuring consistency and comparability in financial reporting.
- Financial accounting information is essential for various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, regulators, and tax authorities, in making informed decisions.
- The accrual method and cash method are two common approaches to financial accounting, with the accrual method being the predominant method for larger, publicly traded companies.
Introduction to Financial Accounting and Its Importance
Financial accounting is key for recording, analyzing, and reporting a company’s financial dealings. It’s different from managerial accounting, which focuses on planning inside the company. Financial accounting can use the accrual method or the cash method. The accrual method records transactions when they happen, while the cash method only records when cash is involved.
Financial accounting follows rules to make sure financial statements are clear and easy to compare. This helps with financial analysis and lets companies be compared fairly. These rules are vital for giving accurate and clear info to users of financial information, like investors and lenders. They need this info to understand a company’s financial health.
Definition and Scope of Financial Accounting
Financial accounting deals with making and sharing important documents for companies. These documents are part of annual reports. They include a balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and sometimes a statement of retained earnings.
Role in Business Operations
Financial accounting is crucial for business success. It provides the financial info needed for smart decisions and tracking performance. It also helps companies follow rules and find ways to get better financially.
Key Stakeholders and Users
Financial accounting info is important to many groups, like investors and lenders. These users of financial information use it to judge a company’s worth and health. This info helps them make better choices.
| Key Financial Statements | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Balance Sheet | Summarizes a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a specific point in time. |
| Income Statement | Reveals a company’s net income by subtracting total expenses from revenue over a specific period. |
| Cash Flow Statement | Focuses on a company’s cash transactions, categorizing them into operating, investing, and financing activities. |
| Statement of Retained Earnings | Shows dividends paid to shareholders and earnings retained by the company over a specific period. |
Fundamental Financial Statements

Financial statements are key in financial accounting. They give a full picture of a company’s financial health and performance. The main ones are the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and shareholders’ equity statement.
The balance sheet shows a company’s financial state at a certain time. It lists assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. For example, ExxonMobil Corporation had $376.3 billion in assets, $163.8 billion in liabilities, and $212.5 billion in shareholders’ equity as of fiscal year 2023.
The income statement, or profit and loss statement, covers a company’s operations over time. ExxonMobil Corporation made $344.6 billion in revenue in fiscal year 2023. It had $291.8 billion in costs, leading to a net income of $36 billion.
The cash flow statement details how a company used cash over a period. It’s divided into operations, financing, and investments. It shows a company’s cash generation and use.
The shareholders’ equity statement tracks changes in a company’s equity over time. It shows the company’s profitability and financing activities.
Together, these financial statements give a full view of a company’s financial health, performance, and cash flow. This helps stakeholders make informed decisions.
| Financial Statement | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Balance Sheet |
|
| Income Statement |
|
| Cash Flow Statement |
|
| Shareholders’ Equity Statement |
|
These financial statements together give a full picture of a company’s financial health, performance, and cash flow. This helps stakeholders make informed decisions.
“Financial statements are the language of business, providing a window into a company’s financial health and performance.”
Financial Accounting Standards and Frameworks

Understanding the financial accounting world means learning about key standards and frameworks. The Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are two major systems. They ensure financial reports are clear and consistent worldwide.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
GAAP is the main accounting rule in the United States. It’s set by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). This framework gives rules for making financial statements. It helps businesses be comparable and standardized.
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) creates the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). More than 140 countries use IFRS. It aims to make financial reports clear and consistent worldwide.
Regulatory Bodies and Their Roles
In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees financial reports. The SEC makes sure companies report accurately. This helps investors make smart choices.
GAAP and IFRS are not the same, despite efforts to align them. They differ in how they measure assets and recognize revenue. Knowing these differences is key for accurate financial reporting and international business.
“The Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting was published by the International Accounting Standards Board (IFRS) in September 2010 with updates in March 2018. The main goal of general purpose financial reporting is to provide valuable financial information to investors, lenders, and others to make informed decisions.”
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) work together. They aim to create a unified Conceptual Framework. This will improve transparency and efficiency in global finance.
Core Accounting Methods and Practices
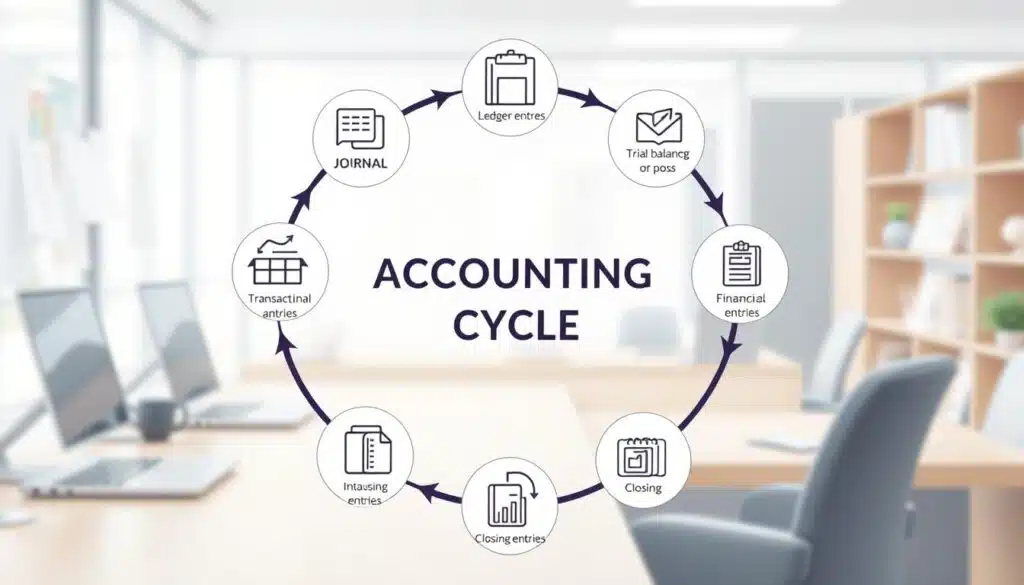
Financial accounting uses different methods to record and report financial transactions. Accrual accounting records revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred. Cash accounting only records transactions when cash is received or paid.
Financial accounting also follows the double-entry bookkeeping principle. This ensures that each transaction is recorded in at least two accounts. The accounting cycle helps maintain accuracy and consistency in financial reports.
Accrual Accounting vs. Cash Accounting
The choice between accrual and cash accounting depends on the business size and complexity. The IRS requires large businesses to use accrual accounting. Small businesses often use cash accounting.
Some businesses use a mix of both methods. This is allowed if they meet certain requirements.
| Accrual Accounting | Cash Accounting |
|---|---|
| Records revenues and expenses as they are earned and incurred | Records revenues and expenses as they are received and paid |
| Utilizes accounts receivable and accounts payable | Does not use accounts receivable and accounts payable |
| More complex, but provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial position | Simpler, but may not provide a complete picture of a company’s financial position |
Accounting practices follow generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). These include the Revenue Recognition Principle and the Matching Principle. They ensure financial reports are accurate and reliable.
These principles are crucial, especially after financial scandals. They highlight the need for ethical and transparent accounting.
Essential Accounting Principles
Accounting principles are the base of financial reporting. They make sure financial statements are trustworthy, easy to compare, and useful for making decisions. Important principles include the revenue recognition, matching, consistency, and conservatism principles.
Revenue Recognition Principle
The revenue recognition principle says income should be recorded when it’s earned. It doesn’t matter when the cash is received. This makes tracking a company’s financial health more accurate over time.
Matching Principle
The matching principle says expenses should be reported with the related revenues in the same period. This gives a clear view of a company’s profit by linking costs to the revenue they help generate. Following this principle is key for good financial analysis.
Consistency and Conservatism
The consistency principle means a company should use the same accounting methods over time. This makes comparisons easier. The conservatism principle suggests being cautious, recognizing expenses before revenues. Other important principles are materiality, which is about reporting significant information, and the going concern assumption, which assumes a business will keep operating.
Also Read : Building Wealth For Financial Independence
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between managerial accounting and financial accounting?
A: Managerial accounting focuses on providing information for internal decision-making, while financial accounting is concerned with reporting financial information to external users. Understanding the differences between managerial accounting vs financial accounting is crucial for students in an accounting course.
Q: Why is financial accounting important for businesses?
A: Financial accounting is important because it provides vital information about a company’s financial performance and position, which is essential for stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and management to make informed decisions.
Q: What modules are included in this financial accounting course?
A: This financial accounting course typically includes modules on the basics of financial statements, preparation of financial statements, financial analysis, and cost accounting, among others.
Q: Who are the primary users of financial accounting information?
A: The primary users of financial accounting information include investors, creditors, management, and regulatory agencies, all of whom rely on basic financial statements for their decision-making processes.
Q: What are the fundamentals of financial accounting that students should learn?
A: Students should learn about the principles of accounting and financial accounting, the preparation of financial statements, cost accounting, and the analysis of financial statements to understand how businesses operate and report their financial activities.
Q: How does cost accounting differ from financial accounting?
A: Cost accounting is a subset of managerial accounting that focuses on capturing and analyzing costs associated with production, while financial accounting deals with the overall financial health of the company, primarily through the reporting of financial statements.
Q: Can financial aid be applied to the accounting and financial accounting courses?
A: Yes, many institutions offer financial aid options for students enrolled in accounting courses, including those focusing on financial accounting and reporting. Students should check with their school’s financial aid office for specific details.
Q: What skills can I expect to gain from a financial accounting course?
A: Students can expect to gain skills in analyzing financial statements, preparing financial statements, understanding accounting principles, and applying basic financial analysis techniques, which are all essential for a career in finance and accounting.
Q: What is the basis of accounting, and why is it important?
A: The basis of accounting refers to the methods used to record and report financial transactions, such as cash basis or accrual basis. Understanding the basis of accounting is important for accurately interpreting financial statements and ensuring compliance with accounting standards.